About the Project
Today, Sierra Leone is ranked 179 out of 182 countries on the Human Development Index, and 117 out of 119 countries on the Global Hunger Index. Poverty remains widespread, particularly concentrated in rural and urban areas outside the capital, with close to 60% of the population living below the poverty line. Poverty is also concentrated among women and young people with around 70% of youth (aged between 15 and 35) unemployed or underemployed. The agriculture sector contributes close to 60% of GDP, with nearly half of the working-age population engaged in subsistence agriculture. However, about 26% of the population is food insecure, unable to afford a basic diet, and has difficulty meeting needs. On average, households spend approximately half of their incomes on food. The climate is generally equatorial with dry and wet seasons. Close to 75% of the country is arable land and is divided between upland and the more fertile lowland areas.
The Government of Sierra Leone developed the Smallholder Commercialization Program (SCP) as part of its National Sustainable Agriculture Development Plan. SCP is a flagship sector program aimed at empowering the rural poor to increase their food security and income on a sustainable basis, leading to long-term economic development and poverty reduction. It focuses on the intensification, diversification, and commercialization of smallholder agriculture through improving value addition and access to marketing. The project provides capacity building to extension workers and farmers utilizing Farmer Field Schools, strengthens agribusiness centers (ABCs) that serve as a bulking center for input and output marketing, equipment rental, and communication and provides technical advisory services for production and processing. SCP provides on-farm water management including the construction of carefully planned structures such as peripheral canals, inlet and outlet structures, etc. that contribute toward the rehabilitation of perennial Inland Valley Swamps (IVS). It also strengthens IVS associations to ensure the maintenance of rehabilitated structures and trains youth contractors to carry out IVS development services. Finally, the project strengthens financial service associations and community banks to increase access to affordable financial services.
Country
- Sierra Leone
Project Status
ClosedFunding
Country-led projectSupervising entity
- IFAD
Call Year
2010GAFSP Funding Amount
50.00Project Highlights

people benefited from the project, 26 percent were women

of increase in farmers' incomes
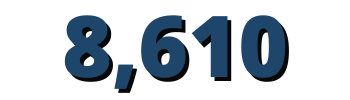
farmers adopted project-promoted technologies
Results
- The project benefitted 158,271 people (26 percent women).
- Incomes increased by 10 percent for farmers, and incomes of select households increased by 38 percent
- SCP improved and rehabilitated irrigation and drainage services for 1,991 hectares of land,
- Provided 7,578 water users with new or improved irrigation and drainage services, 44 percent of whom were women,
- Transformed the 13 cocoa FFSs into farmer-based organizations while rehabilitating 400 hectares of cacao plantations, and created 882 jobs.
- 8,610 farmers adopted project-promoted technologies, and 400 farmers, 40 percent women, benefitted from the transformed FFSs.
Contact
GAFSP Coordination Unit
gafsp-info@gafspfund.org
